Forex Trading Strategies for Different Market Conditions
Forex trading is a dynamic activity that demands adaptability, especially because market conditions frequently change. Traders who succeed in the forex market are those who can adjust their strategies to fit prevailing trends, volatility levels, and economic environments. Understanding and applying appropriate trading strategies for different market conditions is crucial for maximizing profits and managing risks effectively. This article explores several forex trading strategies suited to various market scenarios, helping traders navigate through both trending and ranging markets.
Understanding Market Conditions
Before diving into specific strategies, it is important to grasp the types of market conditions that traders commonly encounter:
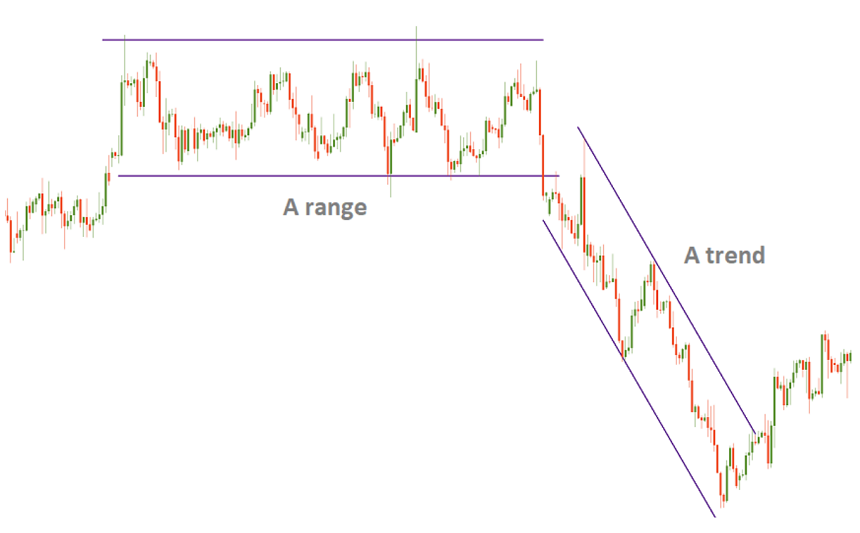
Trending Markets: These occur when currency prices move consistently in one direction—either upward (uptrend) or downward (downtrend). Trending markets are characterized by clear momentum and directional movement.
Ranging Markets: In this condition, price moves sideways within a defined range, oscillating between support and resistance levels without a clear directional bias.
Volatile Markets: These markets show large and rapid price movements, often driven by economic announcements, geopolitical events, or unexpected news.
Low Volatility Markets: These periods exhibit minimal price movement and low trading volume, often occurring during holidays or outside major market sessions.
Different strategies are needed to thrive in each of these environments.
Trading Strategies for Trending Markets
Trending markets offer clear opportunities for traders to ride the momentum. Popular strategies include:
Trend Following: This strategy involves entering trades in the direction of the prevailing trend. Traders use tools like moving averages, trendlines, and the Average Directional Index (ADX) to identify the strength and direction of the trend. For example, a trader might buy when the price is above a rising moving average and sell when below a falling one.
Breakout Trading: Breakouts occur when price moves beyond established support or resistance levels, signaling the start of a new trend. Traders look for significant volume and confirmation through candlestick patterns or technical indicators before entering trades. Breakout strategies capitalize on the momentum generated as the price breaks free from consolidation zones.
Pullback Trading: Instead of chasing the trend’s initial surge, pullback traders wait for the price to temporarily reverse or retrace before entering in the direction of the overall trend. This approach helps achieve better entry prices and reduces risk.
Trading Strategies for Ranging Markets
Range-bound markets require a different approach since there is no clear trend direction. Effective strategies here include:
Range Trading: Traders identify key support and resistance levels and buy near support while selling near resistance. Oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Stochastic indicator are commonly used to spot overbought or oversold conditions within the range.
Mean Reversion: This strategy assumes that price will revert to its average value after extreme moves. Traders look for divergence signals between price and indicators such as the RSI to anticipate reversals within the range.
False Breakout Trading: Sometimes, prices appear to break out of the range but quickly return within it, creating false signals. Skilled traders watch for such fake breakouts to enter positions opposite the initial move, profiting from the return to the range.
Trading Strategies for Volatile Markets
High volatility presents both risk and reward. The following strategies help manage uncertainty:
Scalping: Scalpers make multiple small trades to capture minor price fluctuations. Quick decision-making and tight stop-loss orders are essential to avoid large losses in volatile environments.
News Trading: Economic data releases and geopolitical news can cause sharp price moves. Traders focus on timing entries around such events, either to profit from sudden spikes or to hedge existing positions. Preparation and access to real-time news feeds are critical.
Volatility Breakout: Similar to breakout trading but adapted for volatile markets, this strategy targets large price moves following periods of consolidation or low volatility. Traders use tools like the Bollinger Bands to identify contraction and potential breakout points.
Trading Strategies for Low Volatility Markets
During quiet periods, price movement is subdued, and opportunities can be limited. Strategies that work include:
Range Trading with Tight Stops: Since price swings are small, range trading with closer stop-loss levels helps protect capital while capitalizing on minor fluctuations.
Position Trading: Longer-term traders may use this time to analyze fundamentals and prepare for upcoming market events, holding positions through low volatility periods in anticipation of future moves.
Patience and Reduced Trading Frequency: Sometimes, the best strategy is to reduce trading activity until market conditions improve. This helps avoid unnecessary losses during choppy or stagnant markets.
Adapting to Changing Market Conditions
Markets do not remain static; they shift from trending to ranging, from calm to volatile, often without warning. Successful traders continuously monitor market conditions using tools like:
Technical Indicators: Moving averages, ADX, Bollinger Bands, RSI, and others help identify current trends and volatility levels.
Economic Calendars: Keeping track of scheduled economic releases helps anticipate volatility spikes.
Price Action Analysis: Observing candlestick patterns and chart formations provides insight into potential market reversals or continuations.
Adjusting trading strategies promptly to reflect changing conditions reduces risk and enhances potential rewards.
Risk Management Across All Conditions
Regardless of the strategy or market environment, risk management is fundamental. Setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels, controlling position size, and avoiding over-leveraging help preserve capital through different market phases. Diversification of strategies and instruments can also reduce exposure to sudden market shocks.
Conclusion
Adopting forex trading strategies tailored to specific market conditions is key to trading success. Whether capitalizing on trending moves, navigating range-bound price action, or managing volatile swings, having a clear approach helps traders stay disciplined and responsive. By understanding market behavior and applying the right strategies with solid risk management, traders can enhance their chances of profitability in the ever-evolving forex market. Flexibility and continuous learning remain vital components of a trader’s toolkit for long-term success.



